This blog is the most complete collection of my various posts across the web – with one exception. For 4 years, from 2007 to 2011, I wrote a column for Search Engine Land called “Just Behave” (Danny Sullivan’s choice of title, not mine – but it grew on me). At the time, I didn’t cross-post because Danny wanted the posts to be exclusive. Now, with almost 2 decades past, I think it’s safe to bring these lost posts back home to the nest, here at “Out of My Gord”. You might find them interesting from a historical perspective, and also because it gave me the chance to interview some of the brightest minds in search at that time. So, here’s my first, with Google’s then VP of Search Products and User Experience – Marissa Mayer. It ran in January, 2007 :
Marissa Mayer has been the driving force behind Google’s Spartan look and feel from the very earliest days. In this wide-ranging interview, I talked with Marissa about everything from interface design to user behavior to the biggest challenge still to be solved with search as we currently know it.
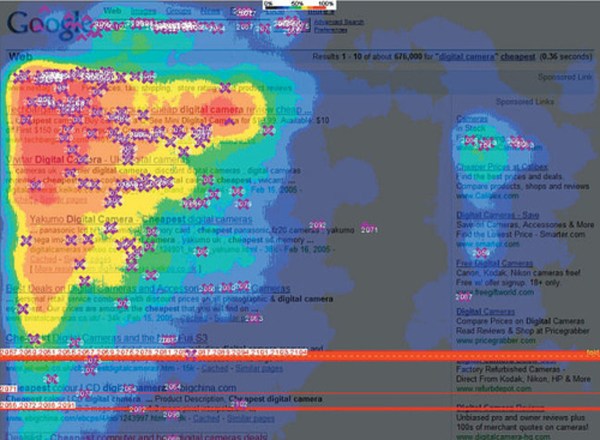
I had asked for the interview because of some notable findings in our most recent eye tracking study. I won’t go into the findings in any great depth here, because Chris Sherman will be doing a deep dive soon. But for the purpose of setting the background for Marissa’s interview, here are some very quick highlights:
MSN and Yahoo Users had a better User Experience on Google
In the original study, the vast majority of participants were Google users, and their interactions were restricted to Google. With the second study, we actually recruited participants that indicated their engine of preference was Yahoo! or MSN (now Live Search), as the majority of their interactions would be with those two engines. We did take one task at random, however, and asked them to use Google to complete the task. By almost every metric we looked at, including time to complete the task (choose a link), the success of the link chosen, the percentage of the page scanned before choosing a link and others, these users had a more successful experience on Google than on their engine of choice.
Google Seemed to Have a Higher Degree of Perceived Relevancy
In looking at the results, we didn’t believe that it was the actual quality of the results that lead to a more successful user experience as much as it was how those results were presented to the user. Something about Google’s presentation made it easier to determine which results were relevant. We referred to it in the study as information scent, using the term common in the information foraging theory.
Google Has an Almost Obsessive Dedication to Relevancy at the Top of the Results Page
The top of the results, especially the top left corner, is the most heavily scanned part of the results page. Google seemed to be the most dedicated of all the three engines in ensuring the results that fall in this real estate are highly relevant to the query. For example, Google served up top sponsored ads in far fewer sessions in the study than did either Yahoo or MSN.
Google Offers the “Cleanest” Search Experience
Google is famous for its Spartan home page. It continues this minimalist approach to search with the cleanest results page. When searching, we all have a concept in mind and that concept can be influenced by what else we see on the page. Because a number of searches on Yahoo! and MSN were launched from their portal page, we wondered how that impacted the search experience.
Google Had Less Engagement than Yahoo with their Vertical Results
The one area where Google appeared to fall behind in these head to head tests was with the relevance of the OneBox, or their vertical results. Yahoo! in particular seemed to score more consistently with users with their vertical offerings, Yahoo! Shortcuts.
It was in these areas in particular that I wanted to get the thinking of Marissa and her team at Google. Whatever they’re doing, it seems to be working. In fact, I have said in the past that Google has set the de facto standard for what we expect from a search engine, at least for now.
Here’s the interview:
Gord: What, at the highest level, is Google’s goal for the user?
Marissa: Our goal is to make sure that people can find what they’re looking for and get off the page as quickly as possible
If we look at this idea of perceived versus real relevancy, some things seemed to make a big difference in how relevant people perceived the results to be on a search engine: things like how much white space there was around individual listings, separating organic results from the right rail, the query actually being bolded in the title and the description and very subtle nuances like a hair line around the sponsored ads as opposed to a screened box. What we found when we delved into it was there seemed to be a tremendous attention to that detail on Google. It became clear that this stuff had been fairly extensively tested out.
I think all of your observations are correct. I can walk you through any one of the single examples you just named and I can talk you through the background and exactly what our philosophy was when we designed it and the numbers we saw in our tests as we had tested them, but you’re right in that it’s not an accident. For example, putting a line along the side of the ad as opposed to boxing it allows it to integrate more into the page and lets it fall more into what people read.
One thing that I think about a lot are people that are new to the internet. A lot of times they subconsciously map the internet to physical idioms. For example, when you look at how you parse a webpage, chances are that there are some differences if there are links in the structure and so forth, but a lot of times it looks just like a page in a book or a page on a magazine, and when you put a box around something, it looks like a sidebar. The way people handle reading a page that has a sidebar on it is that they read the whole main page and then, at the end, if it’s not too interesting, they stop and read the sidebar on that page.
For us, given that we think our ads in some cases are as good an answer as our search results and we want them to be integral to the user experience, we don’t want that kind of segmentation and pausing. We tried not to design it so it looked like a side bar, even though we have two distinct columns. You know, There are a lot of philosophies like that that go into the results page and of course, testing both of those formats to see if that matches our hypothesis.
That brings up something else that was really interesting. If we separate the top sponsored from the right rail, the majority of the interaction happens on the page in that upper left real estate. One thing that became very apparent was that Google seemed to be the most aware of relevancy at that top of page, that Golden Triangle real estate. In all our scenarios, you showed top sponsored the least number of times and generally you showed fewer top sponsored results. We saw a natural tendency to break off the top 3 or 4 listings on a page and scan them as a set and then make your choice from those top 3 or 4. In Google, those top 3 or 4 almost always include 1 or 2 organic results, sometimes all organic results.
That’s absolutely the case. Yes, we’re always looking at how can we do better targeting with ads. But we believe part of the targeting for those ads is “how well do those ads match your query?” And then the other part is how well does this format and that prominence convey to you how relevant it is. That’s baked into the relevance.
Our ad team has worked very very hard. One of the most celebrated teams at Google is our Smart Ads team. In fact, you may have heard of the Google Founder’s Awards, where small teams of people get grants of stock of up to $10,000,000 in worth, split across a small number of individuals. One of the very first teams at Google to receive that award was the Smart Ads team. And they were looking, interestingly enough, at how you target things. But they were also looking at what’s the probability that someone will click on a result. And shouldn’t that probability impact our idea of relevance, and also the way we choose to display it.
So we do tend to be very selective and keep the threshold on what appears on the top of the page very high. We only show things on the top when we’re very very confident that the click through rate on that ad will be very high. And the same thing is true for our OneBox results that occasionally appear above the top (organic) results. Larry and Sergey, when I started doing user interface work, said we’re thinking of making your salary proportional to the number of pixels above the first result, on average. We’ve mandated that we always want to have at least one result above the fold. We don’t let people put too much stuff up there. Think about the amount of vertical space on top of the page as being an absolute premium and design it and program it as if your salary depended on it.
There are a couple of other points that I want to touch on. When we looked at how the screen real estate divided up on the search results page, based on a standard resolution, there seemed to be a mathematical precision to the Google proportions that wasn’t apparent on MSN and on Yahoo. The ratio seemed pretty set. We always seemed to come up with a 33% ratio dedicated to top organic, even on a fully loaded results page, so obviously that’s not by accident. That compared to, on a fully loaded page, less than 14% on Yahoo.
That’s interesting, because we never reviewed on a percentage basis that you’re mentioning. We’ve had a lot of controversy amongst the team, should it be in linear inches along the left hand margin, should it actually be square pixelage computed on a percentage basis? Because of the way that the search is laid out linear inches or vertical space may be more accurate. As I said, the metric that I try to hold the team to is always getting at least one organic result above the fold on 800 by 600, with the browser held at that size.
The standard resolution we set for the study was 1024 by 768.
Yes, we are still seeing as many as 30% plus of our users at 800 by 600. My view is, we can view 1024 by 768 as ideal. The design has to look good on that resolution. It has to at least work and appear professional on 800 by 600. So all of us with our laptops, we’re working with 1024 by 768 as our resolution, so we try to make sure the designs look really good on that. It’s obvious that some of our engineers have bigger monitors and bigger resolutions than that, but we always are very conscious of 800 by 600. It’s pretty funny, most of our designers, myself included, have a piece of wall paper that actually has rectangles in the back where if you line up the browser in the upper left hand corner and then align the edge of the browser with the box you can simulate all different sizes so we can make sure it works in the smaller browsers.
One of the members of our staff has a background in physics and design and he was the one that noticed that if you take the Golden Ratio it lined up very well with how the Google results page is designed. The proportions of the page lined up pretty closely with how that Ratio is proportioned.
I’m a huge fan of the Golden Ratio. We talk about it a lot in our design reviews, both implicitly and explicitly, even when it comes down to icons. We prefer that icons not be square, we prefer that they be more of the 1.7:1.
I wanted to talk about Google OneBox for a minute. Of all the elements on the Google page, frankly, that was the one that didn’t seem to work that well. It almost seemed to be in flux somewhat while we were doing the data collection. Relevancy seemed to be a little off on a number of the searches. Is that something that is being tested.
Can you give me an example?
The search was for digital cameras and we got news results back in OneBox. Nikon had a recall on a bunch of digital cameras at the time and we went, as far as disambiguating the user intent from the query, it would seem that news results for the query digital cameras is probably not the best match.
It’s true. The answer is that we do a fairly good job, I believe, in targeting our OneBox results. We hold them to a very high click through rate expectation and if they don’t meet that click through rate, the OneBox gets turned off on that particular query. We have an automated system that looks at click through rates per OneBox presentation per query. So it might be that news is performing really well on Bush today but it’s not performing very well on another term, it ultimately gets turned off due to lack of click through rates. We are authorizing it in a way that’s scalable and does a pretty good job enforcing relevance. We do have a few niggles in the system where we have an ongoing debate and one of them is around news versus product search
One school of thought is what you’re saying, which is that it should be the case that if I’m typing digital cameras, I’m much more likely to want to have product results returned. But here’s another example. We are very sensitive to the fact that if you type in children’s flannel pajamas and there’s a recall due to lack of flame retardation on flannel pajamas, as a parent you’re going to want to know that. And so it’s a very hard decision to make.
You might say, well, the difference there is that it’s a specific model. Is it a Nikon D970 or is it digital cameras, which is just a category? So it’s very hard on the query end to disambiguate. You might say if there’s a model number then it’s very specific and if only the model number matches in the news return the news and if not, return the products. But it’s more nuanced than that. With things like Gap flannel pajamas for children, it’s very hard to programmatically tell if that’s a category or a specific product. So we have a couple of sticking points.
So that would be one of the reasons why, for a lot of searches, we weren’t seeing product results coming back, and in a lot of local cases, we weren’t seeing local results coming back?. That would be that click through monitoring mechanism where it didn’t meet the threshold and it got turned off?
That’s right.
Here’s another area we explored in the study. Obviously a lot of searches from Yahoo or MSN Live Search get launched from a portal and the user experience if you launch from the Google home page is different. What does it mean as far as interaction with search results when you’re launching the search from what’s basically a neutral palette versus something that’s launched from a portal that colors the intent of the user as it passes them through to the search results?
We want the user to not be distracted, to just type in what they want and not be very influenced by what they see on the page, which is one reason why the minimalist home page works well. It’s approachable, it’s simple, it’s straightforward and it gives the user a sense of empowerment. This engine is going to do what they want it to do, as opposed to the engine telling them what they should be doing, which is what a portal does. We think that to really aid and facilitate research and learning, the clean slate is best.
I think there’s a couple of interesting problems in the portal versus simple home page piece. You might say it’s easier to disambiguate from a portal what a person might be intending. They look at the home page and there’s a big ad running for Castaway and if they search Castaway, they mean the movie that they just saw the ad for. That might be the case but the other thing that I think is more confusing than anything is the fact that most people who launch the search from the portal home page are actually ignoring and tuning out most of the content on a page. If anything you’re more inclined to mistake intent, to think, “Oh, of course when they typed this they meant that,” but they actually didn’t, because they didn’t even see this other thing. One thing that we’re consistently noticing, which your Golden Triangle finding validated, is that users have a laser focus on their task.
The Google home page is very simple and when we put a link underneath the Google search box on the home page to advertise one of our products, we say, “Hey, try Google video, it’s new, or download the new Picassa.” Basically it’s the only other thing on the page, and while it does get a fair amount of click through, it’s nothing compared to the search, because most users don’t even see it. Most users on our search results page don’t see the logo on the top of the page, they don’t see OneBox, they don’t even see spelling corrections, even though it’s there in bright red letters. There’s a single-mindedness of I’m going to put in my search, not let anything on the home page get in the way, and I’m going to go for the first blue left aligned link on the results page and everything above it basically gets ignored. And we’ve seen that trend again and again. My guess is that if anything, that same thing is happening at the portals but because there is so much context around it on the home page, their user experience and search relevance teams may be led astray, thinking that that context has more relevance than it has.
One thing eye tracking allowed us to pull this apart a little bit is that when we gave people two different scenarios, one aimed more towards getting them to look at the organic results and one that would have them more likely to look at sponsored results, and then look down to organic results, we saw the physical interaction with the page didn’t vary as much as we thought, but the cognitive interaction with the page, when it came to what they remembered seeing and what they clicked on, was dramatically different. So it’s almost like they took the same path through, but the engagement factor flicked on at different points.
My guess is that people who come to the portal are much more likely to look at ads. I like to think of them as users with ADHD. They’re on the home page and they enjoy a home page that pulls their attention in a lot of different directions. They’re willing to process a lot of information on the way to typing in their search, and as a result, that same mind that likes that, it may not even be a per user thing, it may be an of-the-moment thing, but a person that’s in the mindset of enjoying that, on the home page, is also going to be much more likely to look around on the search results page. Their attention is going to be much more likely to be pulled in the direction of an ad, even if it’s not particularly relevant, banner, brand, things like that.
I want to wrap up by asking you, what in your mind is the biggest challenge still to be solved with the search interface as we currently know it?
I think there’s a ton of challenges, because in my view, search is in its infancy, and we’re just getting started. I think the most pressing, immediate need as far as the search interface is to break paradigm of the expectation of “You give us a keyword, and we give you 10 URL’s”. I think we need to get into richer, more diverse ways you’re able to express their query, be it though natural language, or voice, or even contextually. I’m always intrigued by what the Google desktop sidebar is doing, by looking at your context, or what Gmail does, where by looking at your context, it actually produces relevant webpages, ads and things like that. So essentially, a context based search.
So, challenge one is how the searches get expressed, I think we really need to branch out there, but I also think we need to look at results pages that aren’t just 10 standard URLS that are laid out in a very linear format. Sometimes the best answer is a video, sometimes the best answer will be a photo, and sometime the best answer will be a set of extracted facts. If I type in general demographic statistics about China, it’d be great if I got “A” as a result. A set of facts that had been parsed off of and even aggregated and cross validated across a result set.
And sometimes the best result would be an ad. Out of interest, when we tracked through to the end of the scenario to see which links provided the greatest degree of success, the top sponsored results actually delivered the highest success rates across all the links that were clicked on in the study.
Really? Even more so than the natural search results?
Yes. Even the organic search results. Now mind you, the scenarios given were commercial in nature.
Right… that makes much more sense. I do think that for the 40 or so percent of page views that we serve ads on that those ads are incredibly relevant and usually do beat the search results, but for the other 60% of the time the search results are really the only reasonable answer.
Thanks, Marissa.
In my next column, I talk with Larry Cornett, Senior Director of Search & Social Media in Yahoo’s User Experience & Design group about their user experience. Look for it next Friday, February 2.